FULL WIDTH PAGE ONE
Good choice.
Joomla! is an excellent Content Management System.
You can, though, spend a lot of time figuring out how (or where) to add, organize, and present your content. ☹
Or you can read on … ☺
If you need to install the Joomla! CMS, software and instructions are HERE.
Menu Item Type: Articles > Category Blog ... description, 6 leading, 36 intro
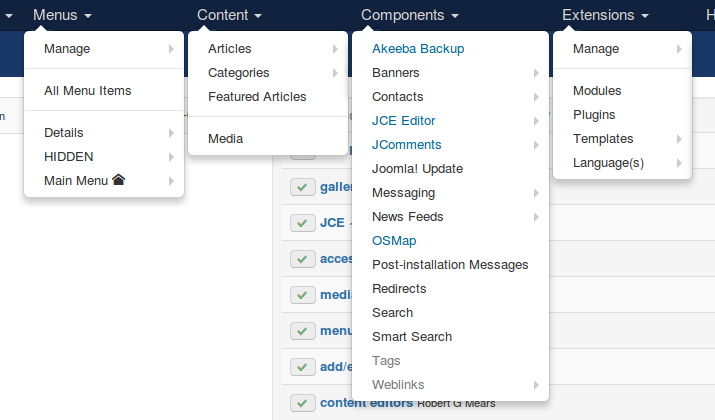
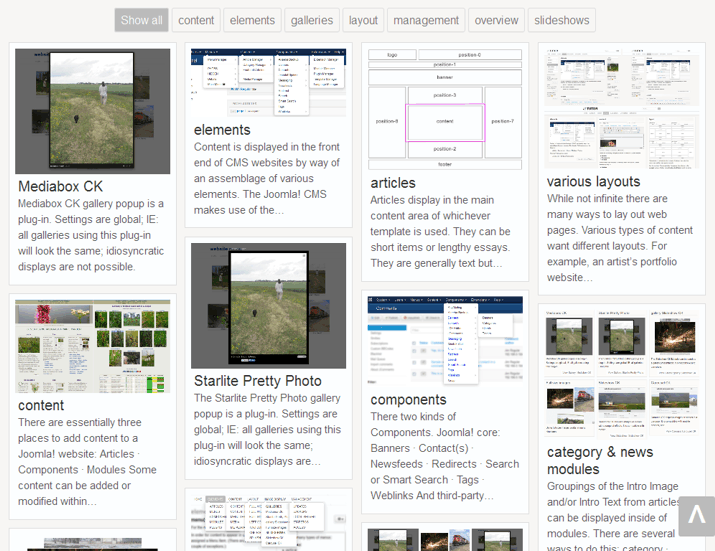
Content is displayed in the front end of Content Management System (CMS) websites by way of an assemblage of various elements. The Joomla! CMS makes use of the following:
Menus • Articles • Components • Modules • Plugins
For which there are two kinds:
Joomla core • third-party extensions
Using this array of elements may be fairly straightforward or quite complicated depending on the nature of your content and what you want your website to do.

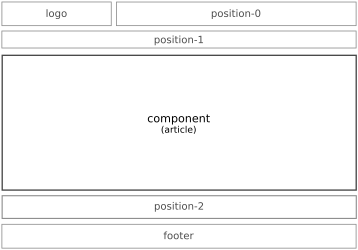
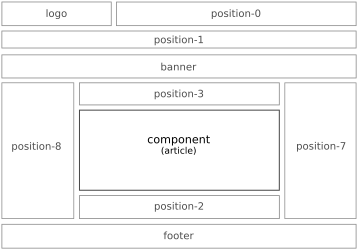
The backbone of one’s presentation is the layout of the website. The structure is determined by the site’s template which is the index.php file in the templates/template_name folder of the site’s system files. This website is built with a slightly modified version of the stock Protostar template.
Regardless of which template is used, the main content of each page — Article(s), Category Description(s), Component, etc — displays in the component area of the page. Most other content is presented by way of Modules which are set to display (or not) on individual pages. How it all displays is determined by CSS specifications.
Examples of various layouts are presented in this section.
Everything displayed in the front end of a website is “content”. Text, images, videos, links … it’s all content. Where it displays is determined by the element used to create it. There are essentially three places to add content to a Joomla! website:
Articles · Components · Modules
Some content can be added or modified within Articles and Custom Modules by way of:
Modules · Plugins
Finding content — in the front end — is usually done by way of the website’s navigation:
Menu(s)

Images can be displayed in a variety of ways:
inside of articles
as galleries
as slideshows (aka rotators or sliders)
randomly in a Module
as page or element backgrounds
They are treated separately because there are so many variables.
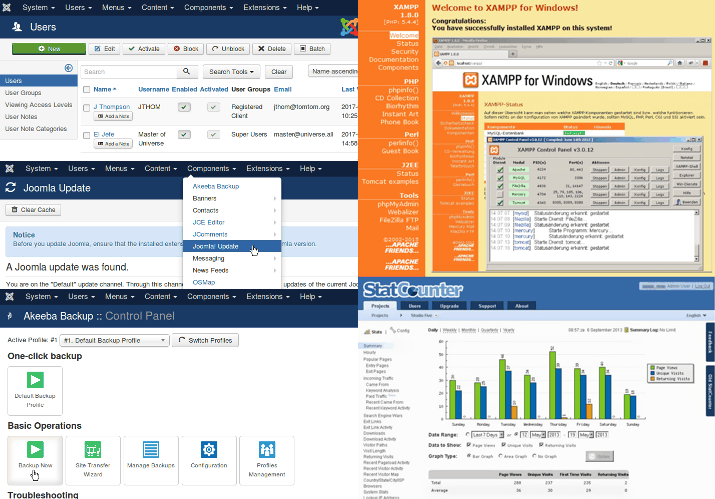
A Content Management System (CMS) website has two parts:
system files • database
Part of the process, in hosting a website, is to:
keep system files up to date
backup the database when changes are made to the site’s content
Another thing to consider is monitoring traffic. It’s good to know how the website is being used.
As well, site security and/or access may be factors.

There are thousands of third-party extensions for the Joomla! CMS which can be used to augment or spruce up content in a website. They come in the form of:
Components · Modules · Plugins
Many extensions are free to use. Many have both a free and a paid version (with more functions). Most require a nominal sum for their use.
A number of extensions have been installed on this website. They are noted on their respective pages:
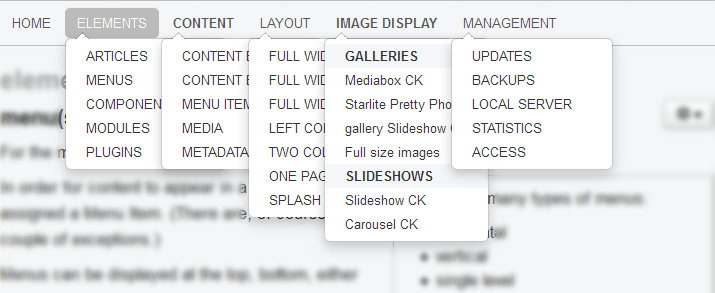
For the most part, website navigation is handled by a Menu.
In fact, generally speaking, for content to display in a Joomla! website it must be assigned to a Menu by way of a Menu Item. (There are, of course, a couple of exceptions; blog posts being one of them.)
Menus are created in the Admin section. Menus can be displayed at the top, bottom, either side, or inside of content. The Main Menu for this site, for example, is a horizontal, multi-level, dropdown at the top of every page (except the SPLASH PAGE where the menu is single level at the bottom). Where a Menu displays is determined by the Module used for the purpose. (Menus must be asigned to a Menu Module in order to display.)
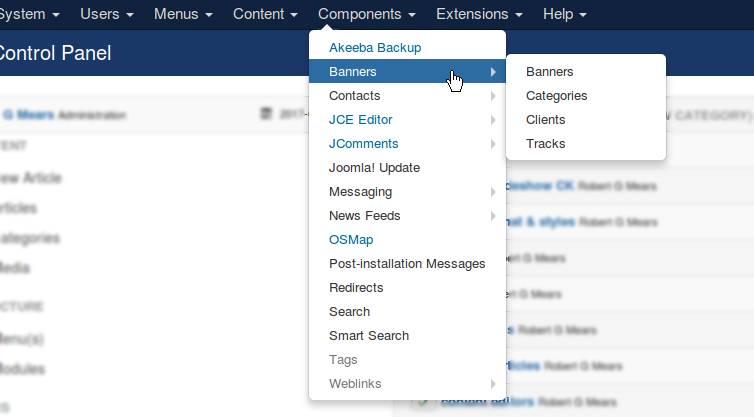
There two kinds of Component.
Joomla core:
• Banners • Contact(s) • Newsfeeds • Redirects • Search or Smart Search • Tags • Weblinks
And third-party Extensions (some of which are installed on this website):
• AcyMailing • Akeeba Backup • JCE Editor • JComments • OSMap • Minitek Wall • DM Pinboard • Gallery WD • ReDJ • Regular Labs Extension Manager
They are all accessible by tapping on “Components” in the Admin Menu in the “back end”.
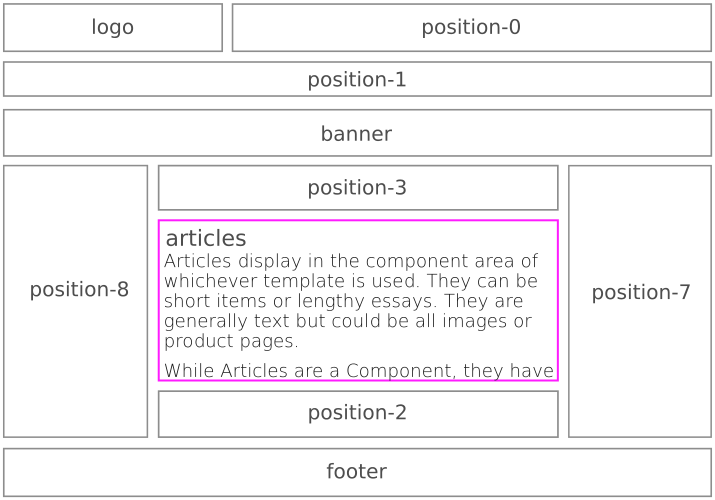
Articles display in the component area of whichever template is used. They can be short items or lengthy essays. They are generally text but could be all images or product pages.
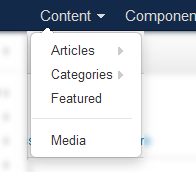
While Articles are a Component, they have their own section in the Administration area of a Joomla! website. They are assigned to Categories which makes it possible to display select groups of content in various ways.
Articles can be full length or split into two areas:
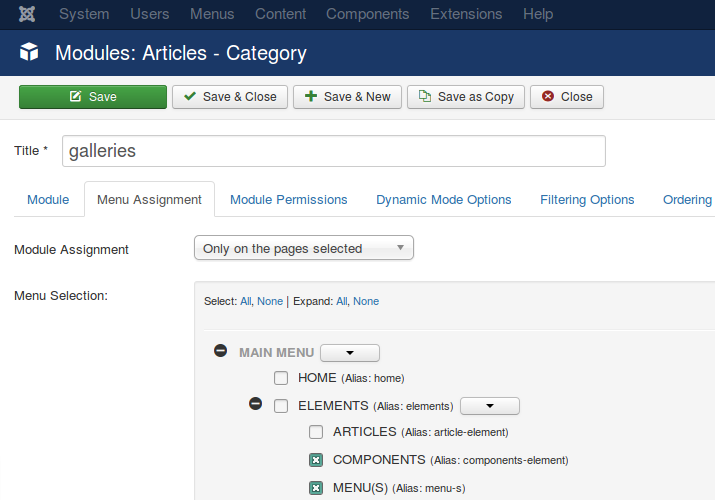
Modules are generally placed in a “layout position” and set to display (or not) on desired pages using “Menu Assignment” in the respective Module’s settings. They can also be displayed inside Articles and Custom Modules (using loadposition or loadmodule).
Modules are accesible under:
Extensions > Modules > New
Existing Modules can be modified from the Modules page.
26 Modules come with Joomla’s core files. There are countless third-party modules, some of which have been installed herein.
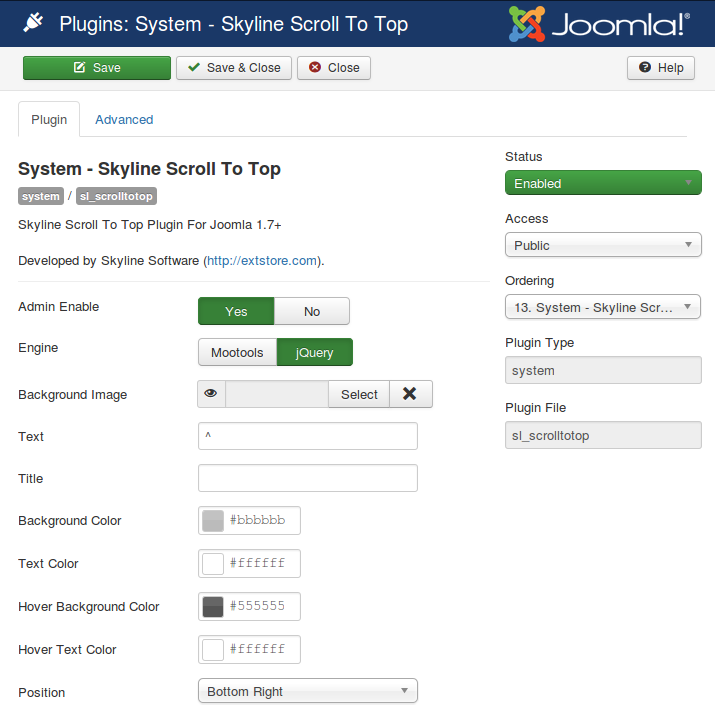
There are close to 60 Joomla! core plugins and a variable number of third-party plugins (depending on which are installed on a given website).
Most plugins are simply enabled or disabled. Those used here are marked: .
Some have a variety of settings — — to control or modify what they do.

The first thing to do after installing Joomla! and logging in to the Admin section is to copy the front end template. It doesn’t matter whether you are using the Protostar template — which ships with Joomla! — or a third-party template that you’ve downloaded and installed. Either way, the original needs to be left intact because template files may change when system files are updated. Which means if you modify the original template files your changes might be overwritten.
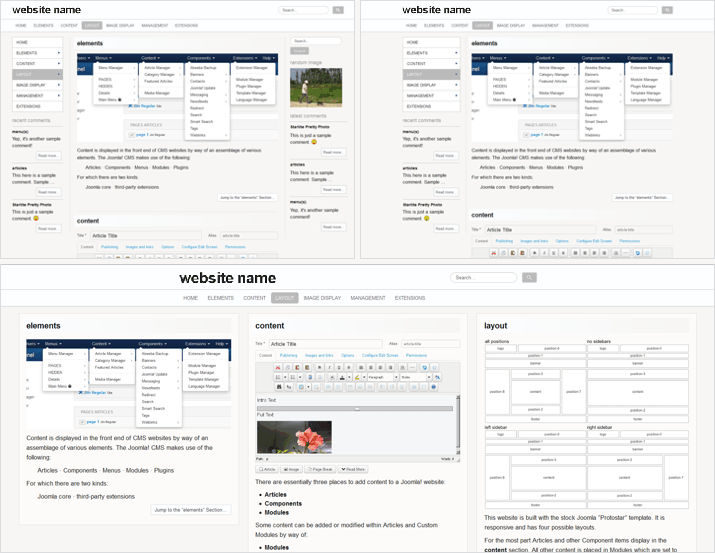
While not infinite there are many ways to lay out web pages. Which is good because various types of content want different layouts.
For example, an artist’s portfolio website may benefit from full width pages without sidebars, while a news or information website tends to work better with a left or right sidebar beside the main content, or with sidebars on both sides, as the case may be.
Organization of page layouts is determined by two things:
The Page Type assigned to the Menu Item (which may or may not have options).
Whether Modules are assigned on the left, right, or both sides of the content area.
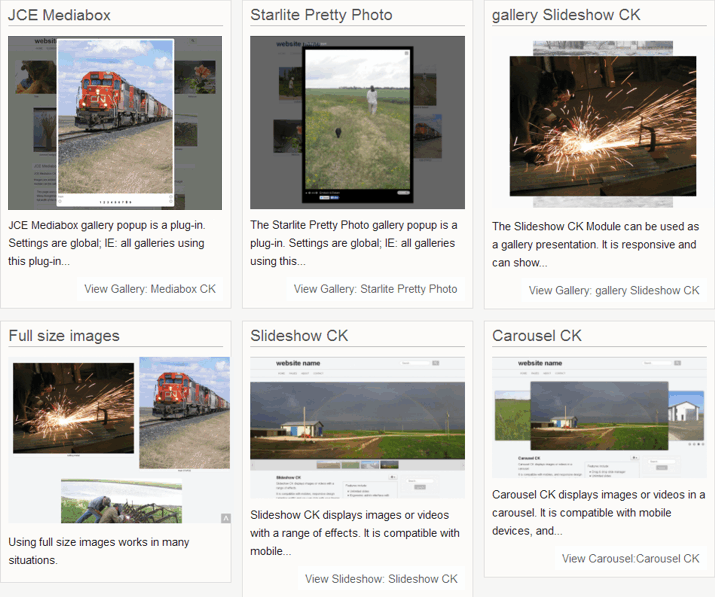
Groupings of the Intro Image and/or Intro Text from articles can be displayed inside of modules.
There are several ways to do this:
category · newsflash
And both Joomla core and third-party Modules for the purpose.
There are many third-party Modules which display “sortable” blocks of Intro Image and/or Intro Text from articles. Two “free” modules are presented here. They both have paid versions which add more functionality. One is also a Component and can be displayed as its own page.

A current trend in web design is a one page layout which often makes use of what is called the parallax effect. A for example is presented here.

Splash (or landing) pages are sometimes used to first introduce a site or a section. They are like covers on a book. Whether to use them is dependent on the nature of the content and a site owner’s preference. A simple example is presented here.
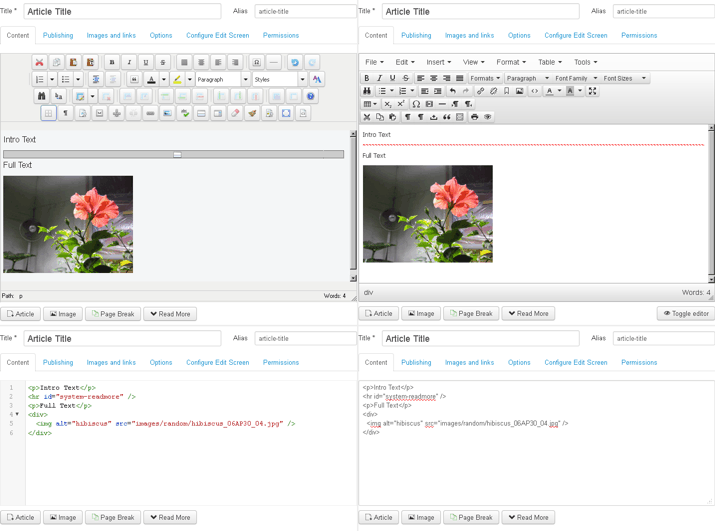
There are four choices of content editor installed on this website. The first three (shown below) come with Joomla’s core files. The fourth is a third-party extension:

There are two places to add or edit articles:
front end · backend
While articles can be added from the front end, assigning menu items to them is done in the backend.
In order to create articles in the front end of the website a “Create Article” menu item must be assigned to a menu. (This can be set to display only for Special or Registered users.)
Articles that are already posted can be edited in the front end by whomever has requisite editing privileges.

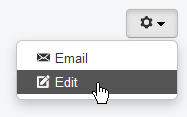
When logged in and viewing the website an optional button, over to the right, is visible for articles that are already published.
Tapping on it causes a dropdown list to appear. Selecting Edit will open the item in an editor panel.
The Edit option only works on articles to which
a respective user has editing access.
article information
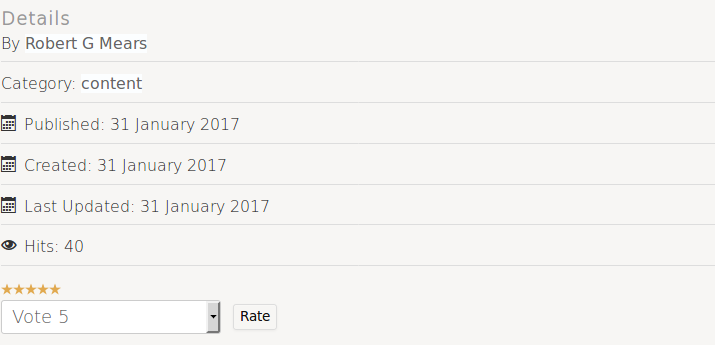
The information presented above is optional.
- By Author Name
- Category: title
- Published: Date
- Created: Date
- Last Updated: Date
- Hits: #
While also optional the Vote dropdown and stars display separately.
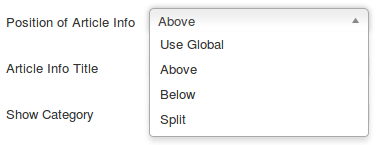
The first group can be displayed at the top or bottom of the page. Or split:
Above the magenta line displays at the top.
Below the line displays at the bottom.
- Category: content
There are two kinds of access to a Joomla! CMS website:
backend · front end
They are different.
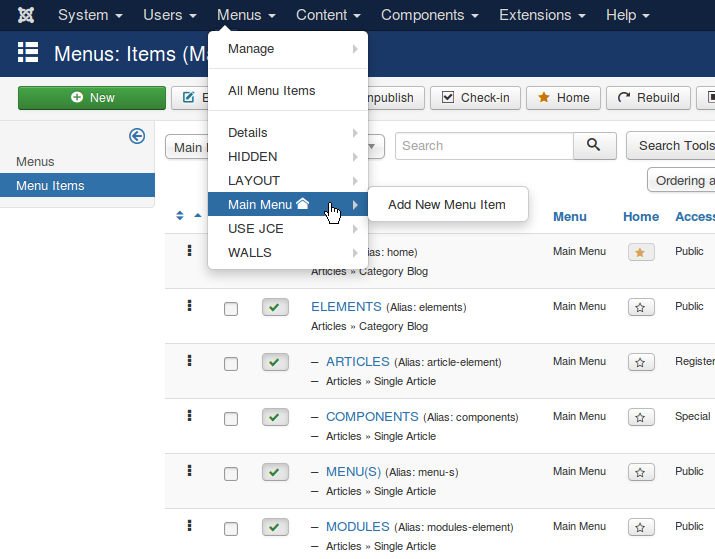
When the Joomla! CMS is first installed the Main Menu is created.
Assigning Menu Items to articles and Component content is done in the backend (or Administration section) of the website under:
Menus > Title of Menu (eg: Main Menu) > Add New Menu Item
(or the New button at the top left of the Menu Items page).
Editing existing Menu Items is done from the same page, just go to the Menu of choice and select the Item you want to edit.
Secondary Menus can be created under:
Menus > Menu Manager > Add New Menu
(or the New button at the top left of the Menu Manager page).
Editing Menus is in the same place but you must check the Menu you want to edit and then tap the Edit button at the top of the page.

There are three ways to add media (images, videos, etc) to a Joomla website:
while editing content such as an Article or Custom Module
through the Media Manager
uploading via FTP by way of a separate program (FileZilla)
The Media Manager is one of Joomla’s best features.
while editing content
Place the cursor where you want the image to appear and tap on the Image button at the bottom of the editor panel:

Metadata is the information that Search Engines look for first. It appears in the HEAD section of a web page. If you want pages on your website to be found by Google, et al, then entering a description and keywords on relevant pages is essential. You can ignore this section if being found by the BOTs, as they’re called, doesn't matter to you.
web host
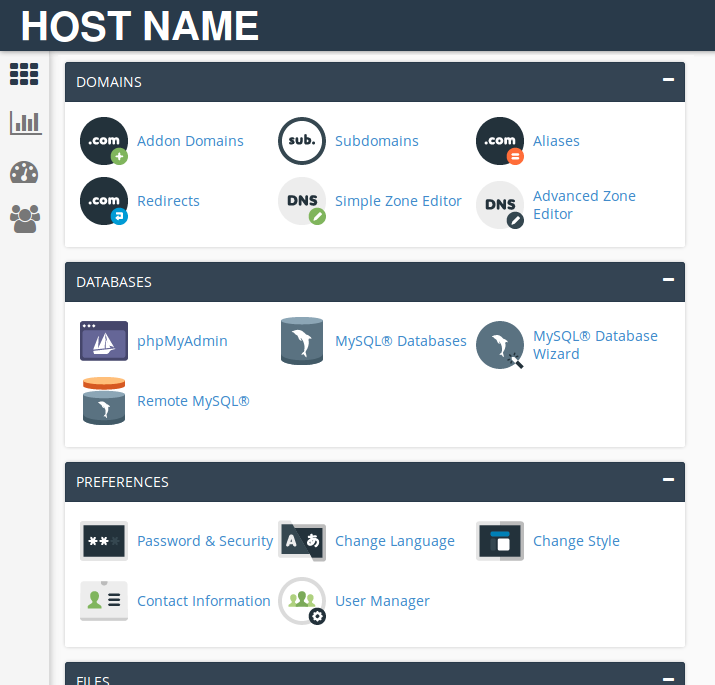
Before setting up a website — whether built with Joomla! or some other CMS — it is necessary to set up a hosting account. If you are using a third-party design or development service your initial website may start as a sub-domain of the service’s domain. For example, the address for this website is http://www.j-tutor.studiofive.biz
j-tutor is the sub-domain
studiofive.biz is the domain name
Once ready to move your site to its own domain you must first have a registered domain name and then have an account with a web host.
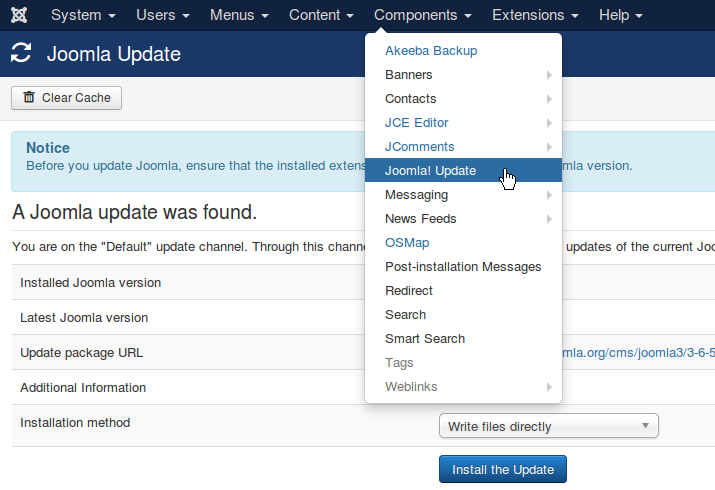
Whether proprietary or open source, the software used to create and maintain websites is constantly being improved. As such, Content Management Systems require periodic updates to the system files.
Expect at least one update per year with the Joomla!® CMS; sometimes two. (WordPress and Drupal are about the same.) As well, concurrent with improvements to the core files, most third-party extensions are also improved on by their respective developers. So, coincident with updating system files, it is prudent to also update the files for extensions used on the website.
Most of the time these updates are painless. Occasionally things go wrong. Hence, it is best to have this done by the person who assembled the site.
backups
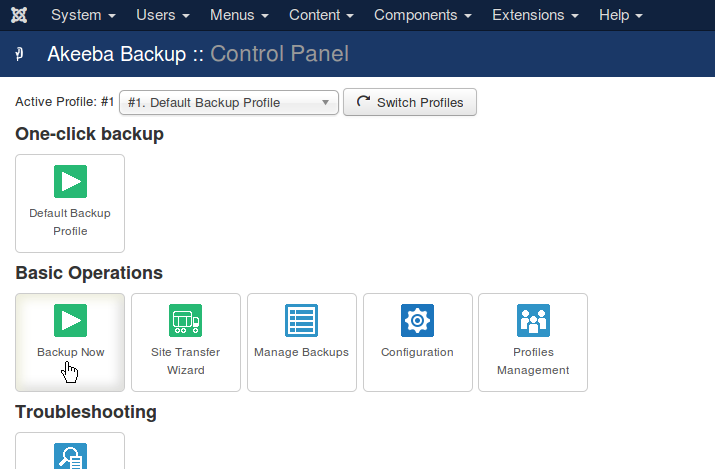
There are essentially two ways to back up a Joomla! website:
long method
short method
local server
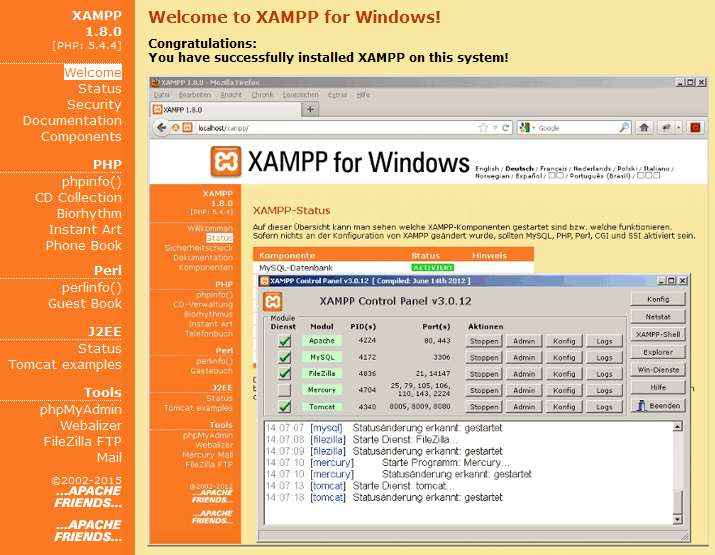
In order for a Content Management System (CMS) website to display, the content must be served to the web browser by a web server. The Apache Server is widely used. It is what serves web pages from the hosting service used by studio five.
For developing websites and testing backups I use what is called a local installation server. There are several variations. XAMPP, the one I use, works on Windows Operating Systems. It uses the Apache Server and runs with PHP.
statistics
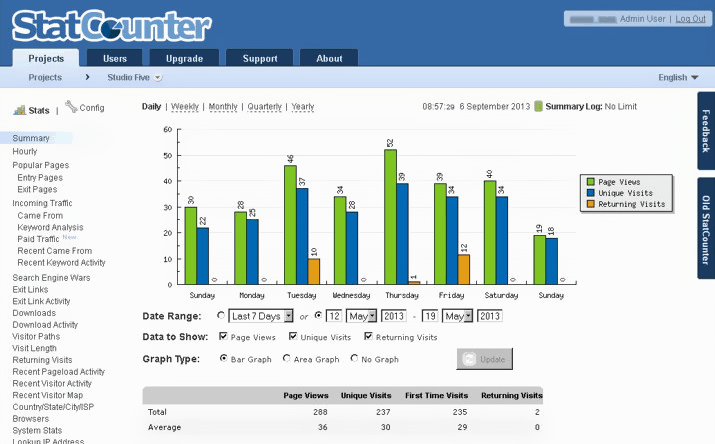
Making use of an extension or a third-party service to monitor traffic to a website is recommended. There are, of course, a variety of options.
security
Website security applies to both the front end and backend. Any website can be password protected in cPanel so that only Users with assigned permission can access a site. That is often the way websites are developed when using a third-party design or development service. However, when a site goes public this protection is removed.
Depending on the site’s content several layers of protection come into play:
- SSL certificates
- robots.txt
- .htaccess
- Admin Tools
- User Management
Tapping on the box below displays how this page is set up.